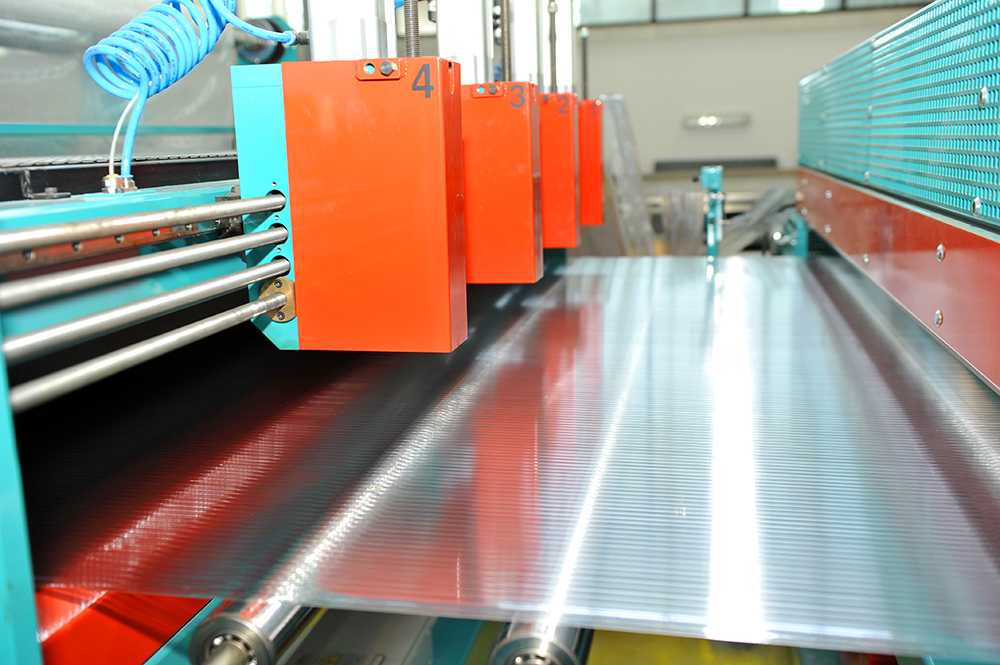
Polycarbonate sheets
Additionally, the enterprise produces cellular polycarbonate sheets and their connector profiles with the help of modern technological equipment of company “Omipa” in Italy. The cellular polycarbonate panels used in facade and roofing systems are the newest products of the plant.
Preferences of polycarbonate to other materials:
- High impact resistance – polycarbonate sheets are 200 times resistant than glass, 8 times resistant than plastics with acrylic. This material is so steady, thus it endures hits of stone and hammer without harming. Warehouses covered with these materials hold harmless at the time of hurricane.
- Light weight – polycarbonate sheets are 16 times light than glass in the same width, 3 times light than plastics with acrylic;
- High thermal insulation; thermal conductivity is low, durability to thermal conductivity is high different from glass consisting of a layer, that is why it reduces 30-50% of energy consumption at the time of heating and cooling.
- High light transmittance – transparency is up to 86%. It is excellent material for maximum light transmittance. Light sprinkles passing through double sheets and doesn"t make a shadow.
- High acoustic insulation – this value depends on width of sheets, average light transmittance is 16-26 dB.
- Longevity – polycarbonate does not change its own physical-mechanical and temperature characteristics during guarantee term (10-12 years) and a long time.
- Secure glazing – sheets prepared from polycarbonate are not broken, fractured because of being polymer main component of polycarbonate and do not make massive break-up as a result of any influences.
- Protection from UV radiation – special protective layer on sheets prevents entering inside of UV radiation.
Specific characteristics of cellular polycarbonate sheets:
- Lightness of cellular polycarbonate sheets enables to prepare original constructions, increases volume of illumination area, performs set-up without help of lifting mechanisms.
- Reducing cost price of object built, application of cellular polycarbonate decrease total cost price of construction object, as well as, light weight of layers enables volume of buildings.
- Easy processing – it is possible to give any shape to layers by cutting them with simple edge tools.
- Resistance to chemicals – cellular polycarbonate sheets are resistant to influence of great numbers of chemicals and compounds.
- Easy cleaning – cellular polycarbonate sheets are easily cleaned with help of water and cotton ( use of cleaning agents are sometimes allowed, though cleaning of polycarbonate with chemicals consisting of ammonium is not recommended, they affect polycarbonate).
- One of the characteristics of polycarbonate sheets that make use of them important in building industry is being practical in all climatic conditions, for example, features of material is not changeable in -50 °C / + 120 °C, it is differ by resistance to changing of high temperature. Polycarbonate sheets using especially for warehouses endures winter's deathly freezing without additional protection actions.
Application areas of cellular polycarbonate in agricultural sector:
- Greenhouses
- Winter gardens
- Warehouses
STP offers high quality polycarbonate sheets with width of 4 mm–40 mm. Application areas of cellular polycarbonate sheets depending on their width are following:
- 4 mm – winter gardens, greenhouses, ceiling floors and advertising constructions (exhibition stands and showcases)
- 6 mm – it has a large application area(sunshade, greenhouses, stained glass);
- 8 mm – it has a large application area (cellulars, sunshade, greenhouses, roofs);
- 10 mm – for overall glazing of vertical and partially horizontal of surfaces (zenith lamps, soundproof fences for freeways);
- 16 mm – for large ceilings with spans (buildings, devices);
- 20 mm – glazing of stadiums, sport tools, pools, pedestrian crossings, coverings of bus stations, pergola windows and verandas.
Technical parameters of polycarbonate
Features | The width of layers, mm | |||||
4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 20 | |
Weight, kg/m2 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 3.1 |
Minimal radius of bending, m | 0.7 | 1.05 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 3.5 |
Sound isolation, dB | 16 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 23 |
Resistance in thermal transmittance R, m² °С/Vt * | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.37 |
Thermal resistance coefficient, Vt/m²х°К * | 4.1 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 1.8 |
Light conductivity (for colorless and transparent layers) | 84 | 82 | 82 | 80 | 76 | 79 |
Swallowing of impact energy, Nm | 21.3 | 27 | >27 | >27 | >27 | >27 |
Standard length of layer, m | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
Width of layer, m | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
POLYCARBONATE PROFILES
Polycarbonate profiles is considered especially for setting up of cellular polycarbonate sheets. Bending radius of profiles, coefficient of thermal expansion are all the same with these parameters.
Polycarbonate profiles have high steadiness and lightweight, transmit light well, and is durable to UV radiation.
Connector profiles are used in building of covering with long distance, covering works of half-dark roofs for transmittance of light rays from connecting area of sheets. Profiles are covered with special protective coverings to protect from radiation rays of sun.
Preferences of polycarbonate profiles: transmittance of light rays in joint of polycarbonate sheets: light weight: bending capability and shaping of watertight coverings.
Technical characteristic:
Type of profile | Weight of profile, q/m | Geometrical dimensions, mm | Thickness of profile wall, mm | Length of profile, m | ||
A | B | |||||
Non-removable connector profiles | ||||||
HP 4-6 | 106 | 8.76 | 52.55 | 0.71 | 6 | |
HP 8 | 183 | 11.3 | 68.72 | 0.93 | ||
HP 10 | 277 | 14.04 | 84.89 | 1.15 | ||
Type of profile | Weight of profile, q/m | Geometrical dimensions, mm | Thickness of profile wall, mm | Length of profile, m | ||||
A | B | |||||||
Removable connector profiles (cover+base) | ||||||||
HP 8-16 | 184 | 18.6 | 60.0 | 1.2 | 6 | |||
HP 8-10 | 166 | 16.4 | 62.0 | |||||
HP 16 | 206 | 23.0 | 62.0 | |||||
Type of profile | Weight of profile, q/m | Geometrical dimensions, mm | Thickness of profile wall, mm | Length of profile, m | |||||
A | B | ||||||||
Closure profile | |||||||||
UP 4 | 50 | 6.82 | 24.0 | 0.9 | 6 | ||||
UP 6 | 64 | 9.0 | 25 | 1.0 | |||||
UP 8 | 68 | 11 | |||||||
UP 10 | 70 | 13.0 | |||||||
UP16 | 72 | 19.0 | |||||||
Non-removable connector profiles
Non-removable connector profiles are used firstly in polycarbonate profiles with small construction which joint of distance is shorter. This profile is ideal for connecting of polycarbonate panels vertically (office partitions, advertising tires, light box)
Removable connector profile
It ensures rapid and reliable connecting of profiles with framework between themselves. Profile consists of two parts: lower part- “base” and upper part- connective “cap”.
Closer polycarbonate profile
This kind of polycarbonate profiles are intended for closing ends of polycarbonate sheets and connecting tightly. Closer polycarbonate profiles protect from break-up, bending, and other deformations by edging ends of layers, as well as, remove condensate arising inside of cellulars. This kind of profiles are also used for edging ends of layers having appropriate thickness and prepared from hard materials.
POLYCARBONATE PANELS HAVING CLOSER JOINT
These panels having a service life of 50 years are used for several aims, especially construction of roofs. They are unreplaceable in the regard of effective using solar light and saving electrical energy. Closure joints of polycarbonate panels ensure tight binding with sandwich panels and one other.
Technical characteristic:
Thickness of panels, mm | 1 m2 weight of panels, kg | Length x width of panels, mm | Coefficient of light transmittance, % | Coefficient of thermal transmittance, Vt/m²х°К |
35 40 | 4.1 4.3 | 12000 x 1000 12000 x 1000 | 68 63 | 1.50 1.45 |
| Panelin qalınlığı, mm | Panelin 1 m2-nin çəkisi, kq | Panelin uzunluğu x eni, mm | İşıqburaxma əmsalı,% | İstilikötürmə əmsalı, Vt/m²х°К |
35 40 | 4,1 4,3 | 12000 x 1000 12000 x 1000 | 68 63 | 1,50 1,45 |